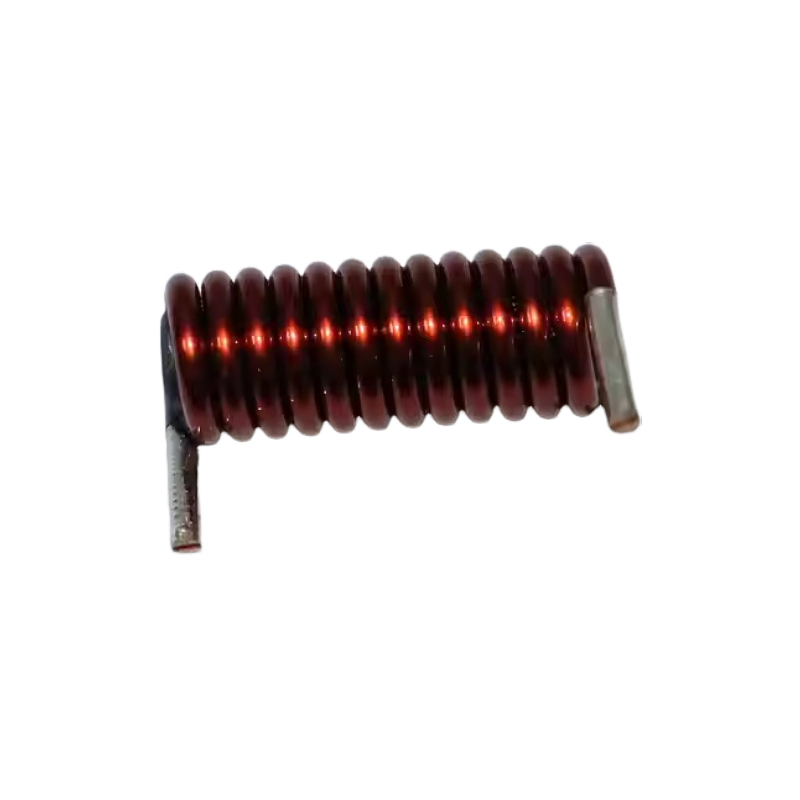
Coil
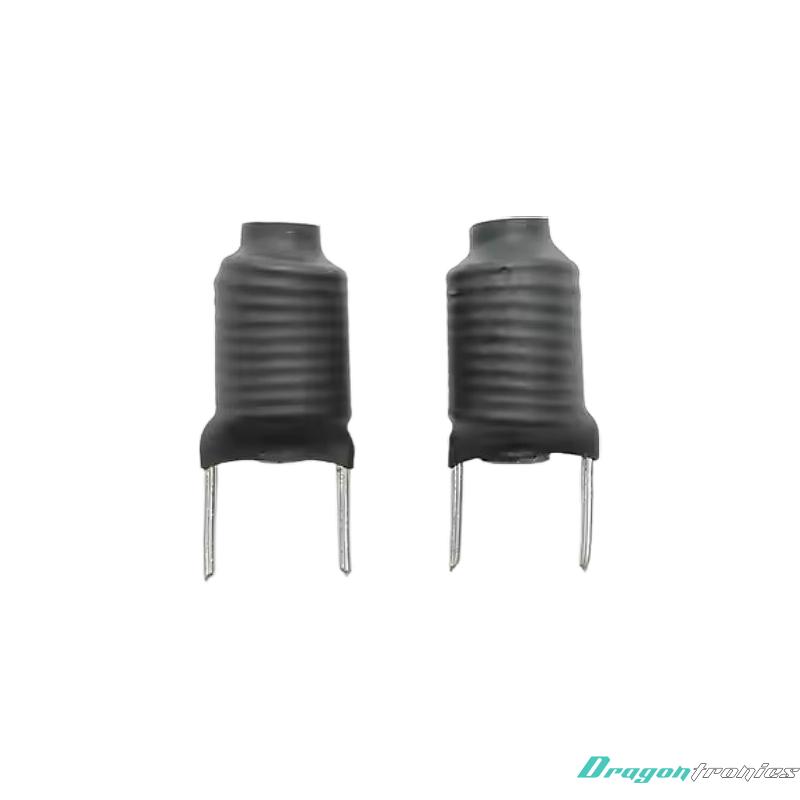
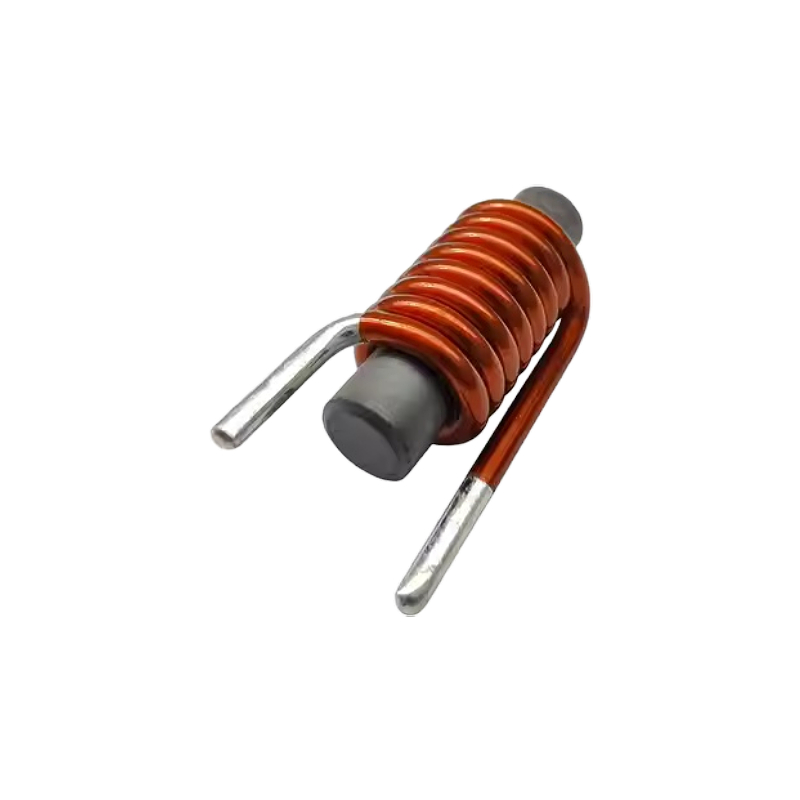
2-PIN THD inductor
- Product description: A 2-PIN THD (Through-Hole Device) inductor is a type of inductor that is designed for use in through-hole mounted applications, where it is inserted into holes on a printed circuit board (PCB) and sol
How a 2-PIN THD inductor works:
1. Working in DC and AC Circuits
· DC Operation: When direct current (DC) flows through a 2-pin THD inductor, it initially resists any change in current. However, once the current has reached a steady state, the inductor behaves like a short circuit (because the magnetic field has stabilized, and there’s no change in magnetic flux). Therefore, in DC circuits, inductors primarily store energy during transitions (like when current is first applied) and smooth out current flow.
· AC Operation: In alternating current (AC) circuits, the current is continuously changing direction, so the magnetic field around the inductor is also continuously changing. The inductor opposes these changes by generating an opposing voltage (due to self-induction). This results in inductive reactance, where the inductor limits the flow of AC, especially at higher frequencies. The higher the frequency, the greater the opposition to the current.
2. Applications of 2-Pin THD Inductors
· Power Supply Filters: In DC-DC converters, buck converters, and boost converters, 2-pin THD inductors are used to smooth out fluctuations and reduce ripples in the output voltage.
· Signal Filters: In audio circuits, RF (radio frequency) circuits, and communication systems, inductors are used to filter out unwanted frequencies or smooth signals.
· Energy Storage: Inductors are used in systems that require energy storage in the magnetic field, such as flyback converters and transformers.
· Chokes: 2-pin inductors can also serve as chokes, which limit the flow of high-frequency AC while allowing DC or low-frequency AC to pass through.
· Inductive Sensing: In applications such as inductive proximity sensors, inductors detect the presence of conductive objects by observing changes in the inductance caused by nearby metals.
3. How the 2-Pin THD Inductor is Mounted on a PCB
· Pin Insertion: The two metal pins of the inductor are inserted into the through-holes on the PCB.
· Soldering: Once the pins are in place, the leads are soldered to the PCB, forming an electrical connection. The solder ensures that the inductor is securely mounted to the board and has good electrical contact.
· Connection to Circuit: The two pins are then connected to the rest of the circuit, such as power lines, ground, or signal paths, depending on the design of the circuit.
Conclusion
A 2-pin THD inductor works by utilizing the principle of electromagnetic induction to store energy in a magnetic field and resist changes in current. It provides inductive reactance in AC circuits and stores energy in magnetic fields in both AC and DC circuits. The two leads allow the inductor to be mounted on a PCB, making it suitable for various applications such as power supplies, signal filtering, energy storage, and chokes. The inductor's key parameters, such as inductance, resistance, and current rating, influence its performance in different electronic systems.
Categories
Latest News
Contact Us
Contact: Fiona Wu
Phone: 86 - 173 28414 818
Tel: 86 - 173 28414 818
Add: 20, Changtian Road, Hengli, Dongguan, Guangdong, 523852, China





 Lankecms
Lankecms lankecms
lankecms
 Lankecms
Lankecms